Here’s a step-by-step tutorial with deep explanations + examples:
📘 Medallion Architecture in Data Lakehouse
(Bronze, Silver, Gold Layers with Databricks)
1. 🔹 Introduction
In a Data Lakehouse (e.g., on Databricks), data pipelines often deal with raw, semi-processed, and business-ready datasets.
To organize this systematically, Databricks (and the Lakehouse paradigm) uses the Medallion Architecture:
- Bronze → Silver → Gold layers
- Each layer adds refinement, cleaning, and value.
- Multi-hop design ensures traceability, scalability, and governance.
Think of it as:
- Bronze = Raw ingestion
- Silver = Cleansed / standardized
- Gold = Business consumption
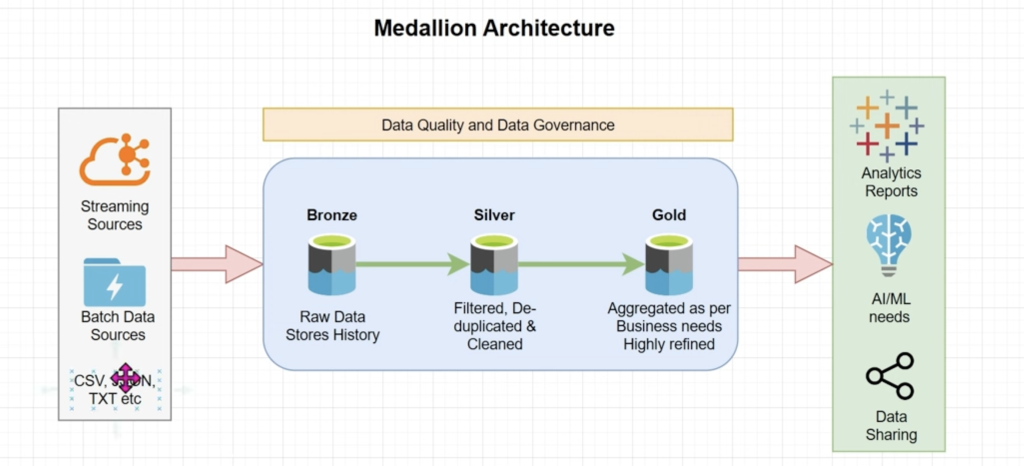
2. 🔹 What is Medallion Architecture?
The Medallion Architecture is a multi-hop pipeline design:
➡ Data flows left to right
➡ Gets cleaner, more refined, and enriched at each stage
➡ Supports auditability, lineage, and governance
Diagram (Conceptual)
Source Systems (files, APIs, streams)
↓
Bronze Layer (Raw)
↓
Silver Layer (Cleansed / Enriched)
↓
Gold Layer (Aggregated / Business-ready)
↓
BI Reports | ML Models | Data Sharing
3. 🔹 Bronze Layer
📌 Purpose:
- Store raw ingested data exactly “as is” from source systems.
- Acts as a single source of truth for history/audit.
- Supports batch, streaming, API ingestion.
Example Sources:
- CSV, JSON, Parquet, Avro
- Event hubs / Kafka / IoT streams
- RDBMS snapshots
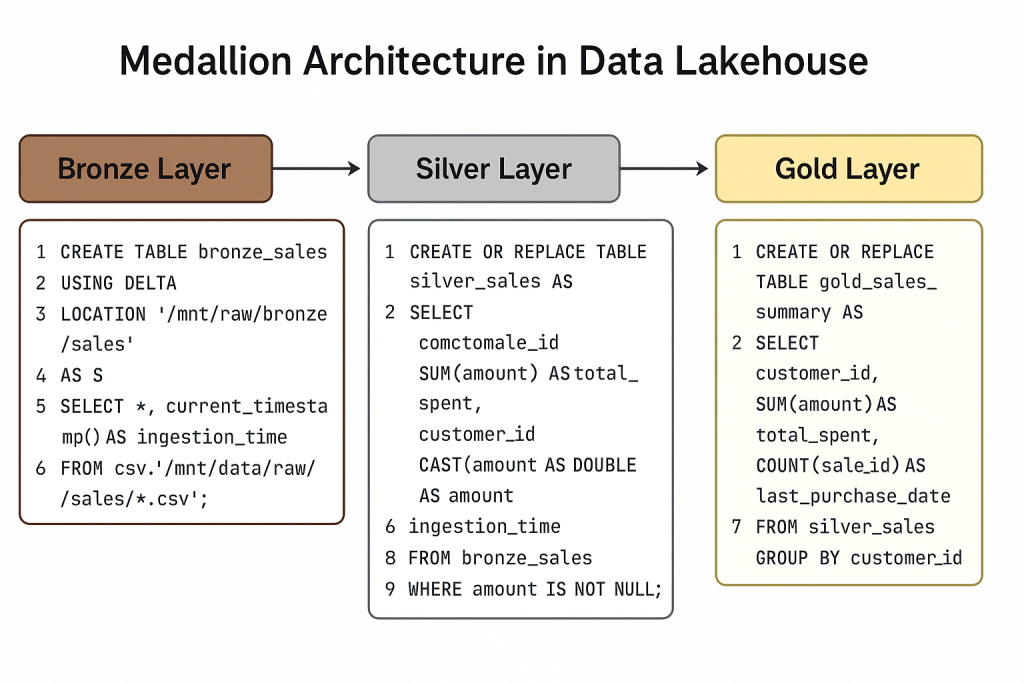
Databricks Example (Bronze Table Creation):
-- Ingest raw CSV files into Bronze layer
CREATE TABLE bronze_sales
USING DELTA
LOCATION '/mnt/raw/bronze/sales'
AS
SELECT *, current_timestamp() AS ingestion_time
FROM csv.`/mnt/data/raw/sales/*.csv`;
✅ Notes:
bronze_saleskeeps raw data.- Added
ingestion_timefor audit & lineage.
4. 🔹 Silver Layer
📌 Purpose:
- Take raw bronze data and refine it:
- Deduplicate
- Filter bad records
- Apply standard schema
- Join with other datasets
Operations:
- Remove null values
- Standardize column names
- Join lookup tables
- Handle schema evolution
Databricks Example (Silver Table Creation):
-- Create Silver layer with cleaned sales data
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE silver_sales AS
SELECT DISTINCT
CAST(sale_id AS STRING) AS sale_id,
customer_id,
CAST(amount AS DOUBLE) AS amount,
to_date(sale_date, 'yyyy-MM-dd') AS sale_date,
ingestion_time
FROM bronze_sales
WHERE amount IS NOT NULL;
✅ Notes:
- Duplicate sales removed with
DISTINCT. - Schema cleaned (
amount → DOUBLE,sale_date → DATE). - Filtering out invalid/null records.
5. 🔹 Gold Layer
📌 Purpose:
- Provide business-ready datasets for:
- BI Dashboards (PowerBI, Tableau, Databricks SQL)
- ML Models
- External data sharing
- Data is aggregated, enriched, and business-friendly.
Typical Transformations:
- Aggregations (SUM, AVG, COUNT)
- Derived KPIs (Revenue, Growth, Retention)
- Star/Snowflake schemas
Databricks Example (Gold Table Creation):
-- Create Gold table for business reports
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE gold_sales_summary AS
SELECT
customer_id,
SUM(amount) AS total_spent,
COUNT(sale_id) AS total_transactions,
MAX(sale_date) AS last_purchase_date
FROM silver_sales
GROUP BY customer_id;
✅ Notes:
- Gold layer is aggregated by
customer_id. - Optimized for BI dashboards & reporting.
6. 🔹 End-to-End Data Flow
- Raw ingestion → Bronze
(Keep data unchanged, add audit columns) - Refine → Silver
(Clean, deduplicate, enforce schema) - Business aggregation → Gold
(KPIs, analytics-ready data)
7. 🔹 Data Quality & Governance
- Apply data validation rules in Silver.
- Use Unity Catalog for governance across all layers.
- Track lineage: Gold → Silver → Bronze → Source.
- Implement audit logs with
ingestion_timeand metadata columns.
8. 🔹 Why Medallion Architecture?
- Scalability: Supports millions of records.
- Flexibility: Same raw data → multiple refined use cases.
- Auditability: Raw always available.
- Separation of Concerns: Each layer has clear purpose.
- Performance: Optimized Delta format + Z-order indexing.
✅ Summary
- Bronze Layer = Raw, historical, unmodified data.
- Silver Layer = Refined, cleansed, schema-standardized data.
- Gold Layer = Business-ready aggregated data.
- Together, they form a multi-hop pipeline that is robust, scalable, and traceable.
🔥 Pro Tip:
In real-world Databricks projects, you’ll often implement this pipeline using Workflows/Jobs, Auto Loader for ingestion, and Delta Live Tables (DLT) for automated Medallion pipelines.