1. Introduction & Overview
🔍 What is Unit Testing?
Unit Testing is a software testing method where individual units or components of a program are tested in isolation from the rest of the system. A unit is typically the smallest testable part of an application, such as a function or method.
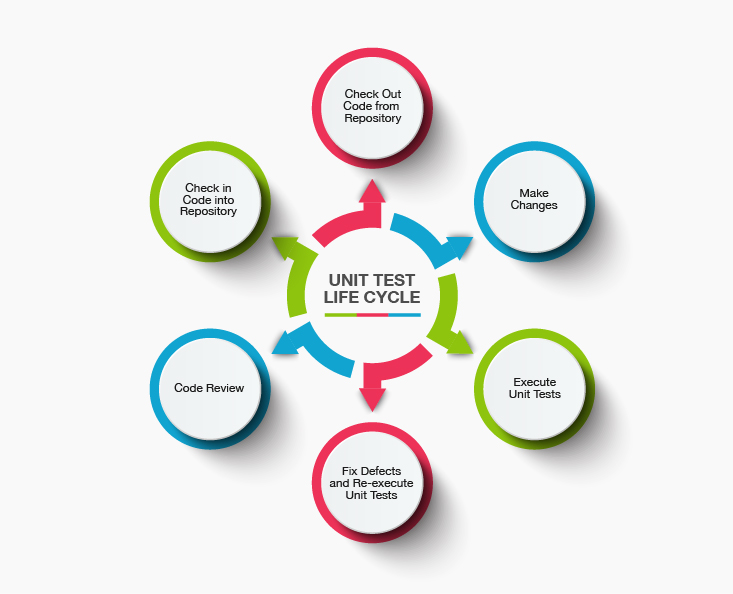
The goal of unit testing is to:
- Validate that each unit performs as expected.
- Detect bugs early in the development cycle.
- Enable continuous integration and delivery by ensuring code quality.
🧭 History & Background
- 1970s: Concept of unit testing emerged alongside modular programming.
- 1990s: Popularized with the rise of Extreme Programming (XP) and Agile.
- Early 2000s: Frameworks like JUnit (Java) and NUnit (.NET) became industry staples.
- Now: Unit testing is deeply embedded in modern DevSecOps pipelines, with support from tools like pytest, Mocha, JUnit, and xUnit.
🛡️ Why is Unit Testing Relevant in DevSecOps?
DevSecOps integrates security into DevOps. Unit testing helps by:
- Catching bugs and vulnerabilities early.
- Preventing security regressions through test coverage.
- Supporting shift-left security practices by enforcing quality gates at the code level.
- Making code more resilient to injection attacks, buffer overflows, or unexpected behavior.
2. Core Concepts & Terminology
📘 Key Terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Test Case | A specific scenario under which a unit is tested. |
| Test Fixture | Setup code required to run one or more tests. |
| Mocking | Simulating the behavior of complex, real objects. |
| Assertion | Statement to verify test success or failure. |
| Code Coverage | Percentage of code exercised by the tests. |
| Regression | A bug that appears after changes, usually in previously working features. |
🔗 DevSecOps Lifecycle Integration
| DevSecOps Phase | Unit Testing Role |
|---|---|
| Plan | Define test strategies and coverage thresholds. |
| Develop | Write unit tests alongside business logic. |
| Build | Integrate test execution in CI pipelines. |
| Test | Automate and validate with test suites. |
| Release | Block release if test coverage falls below thresholds. |
| Deploy | Validate build artifacts using unit test reports. |
| Operate | Monitor test regressions in telemetry/logs. |
| Monitor | Analyze test performance in real time for anomalies. |
3. Architecture & How It Works
🧩 Components
- Test Runner: Executes unit tests (e.g.,
pytest,mocha,unittest). - Assertions Library: Used to define expected results (
assertEqual,expect().toBe()). - Mocks/Stubs: Simulate components like databases or APIs.
- Test Coverage Tools: Measure and report code coverage (e.g.,
coverage.py,Istanbul). - Reporting System: Outputs test results in formats like JUnit XML or HTML.
🔄 Internal Workflow
- Developer writes code and corresponding unit tests.
- Tests are automatically executed in CI/CD pipelines on code commit.
- Failures prevent builds or trigger alerts.
- Results are collected and visualized in dashboards.
🏗️ Architecture Diagram (Text Description)
[Developer]
↓ writes code/tests
[Source Control (e.g., GitHub)]
↓ triggers CI
[CI Tool (GitHub Actions, Jenkins, GitLab CI)]
↓ runs
[Test Runner] → [Codebase]
↓
[Assertions] → [Mocks/Stubs] → [Test Results]
↓
[Reports/Dashboards]
☁️ Integration Points with CI/CD & Cloud
- GitHub Actions:
- name: Run Unit Tests run: npm test - GitLab CI:
test: stage: test script: - pytest - AWS CodeBuild: Include
buildspec.ymlfor test steps. - Azure DevOps: Integrate with
.NET testornpm run test.
4. Installation & Getting Started
⚙️ Basic Setup (Python Example with pytest)
Prerequisites:
- Python installed (
3.8+) - pip installed
pytestpackage
🧪 Step-by-Step Guide
# 1. Create virtual environment
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # or venv\Scripts\activate on Windows
# 2. Install pytest
pip install pytest
# 3. Create a sample test file
touch test_math.py
# test_math.py
def add(a, b):
return a + b
def test_add():
assert add(2, 3) == 5
# 4. Run tests
pytest
Output:
==================== test session starts ====================
collected 1 item
test_math.py . [100%]
5. Real-World Use Cases
🛠️ 1. Secure Microservices in CI/CD
- Unit tests validate logic of each microservice independently.
- Prevent deployment of broken or insecure microservices.
- Tools:
JUnit,pytest,Mocha,Istio,Linkerd.
🏥 2. Healthcare Compliance (HIPAA)
- Unit tests ensure patient data transformations meet standards.
- Example: Validate anonymization routines.
- Supports audit trails via test logs.
💳 3. FinTech Transaction Logic
- Validate financial computations, rounding, and limits.
- Use mocks for 3rd-party payment APIs.
- Regulatory benefit: Proof of due diligence.
🧪 4. Containerized DevSecOps Pipelines
- Run unit tests inside Docker containers.
- Example:
docker run -v $(pwd):/app pytest - Integrate with security scanning tools post-test (e.g., SonarQube).
6. Benefits & Limitations
✅ Key Advantages
- Detect bugs early → save costs later.
- Encourage modular, testable code.
- Fast feedback for developers.
- Enables continuous delivery with confidence.
⚠️ Common Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| False Positives | Poor tests can pass even when bugs exist. |
| Test Maintenance Overhead | Tests must evolve with the codebase. |
| Lack of Coverage | Missed edge cases due to narrow test focus. |
| Security Gaps | Unit tests may not cover integrated vulnerabilities. |
7. Best Practices & Recommendations
🔐 Security Tips
- Validate input sanitation via unit tests.
- Include edge-case tests for buffer overflows, injection attempts.
- Test logic that handles authentication, authorization, or encryption.
⚙️ Performance & Maintenance
- Keep tests atomic: one assertion per test.
- Use mocking to reduce external dependencies.
- Refactor tests with code changes to avoid stale tests.
📜 Compliance Alignment
- Include test logs in audit reports.
- Automate generation of test coverage reports.
- Use tagging (
@secure,@critical) for compliance-critical tests.
🤖 Automation Ideas
- Block PRs with low test coverage via CI rules.
- Auto-generate tests using tools like Hypothesis or Jest Snapshots.
- Integrate static code analysis tools post unit testing.
8. Comparison with Alternatives
| Approach | Scope | Speed | Security Coverage | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit Testing | Functions/methods | Very Fast | Medium | Quick logic validation |
| Integration Test | Modules + systems | Moderate | High | Test module interactions |
| Functional Test | End-to-end flows | Slower | High | Simulate user behaviors |
| Fuzz Testing | Randomized input | Variable | Very High | Test unknown vulnerabilities |
✅ When to Choose Unit Testing
- Early development phase.
- Frequent code commits and merges.
- High-speed test feedback needed.
- Working in CI/CD-focused workflows.
9. Conclusion
📌 Final Thoughts
Unit testing is a cornerstone of modern DevSecOps practices. It ensures that code behaves as intended, supports compliance efforts, and enables high-confidence automation in CI/CD pipelines.
🔮 Future Trends
- AI-powered test generation.
- Self-healing tests in dynamic environments.
- Closer integration with SAST/DAST for unified security feedback.
🔗 Further Resources
- 📘 pytest Documentation
- 📘 JUnit 5
- 📘 Mocha
- 🧑🤝🧑 DevSecOps Community
- 🧪 OWASP Testing Guide
Category: