1. Introduction & Overview
🔍 What Are Data Contracts?
Data Contracts are formal, versioned agreements between data producers and consumers, defining the structure, semantics, and quality expectations of the data being exchanged. Much like an API contract in software, a data contract ensures reliable and predictable data pipelines, minimizing unexpected schema changes and broken workflows.
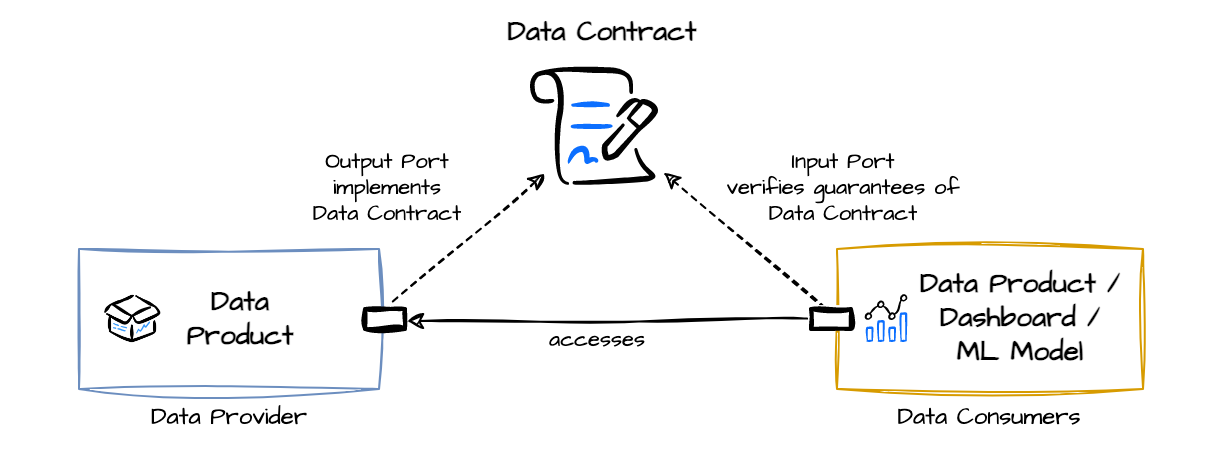
🏛️ History & Background
- Emerged from the evolution of DataOps and Product-Oriented Data Engineering.
- Initially inspired by API design principles, later extended into data ecosystems.
- Gained momentum with modern event-driven architectures and data mesh paradigms.
- Now pivotal in regulated, large-scale DevSecOps environments with strict data governance.
🎯 Why Is It Relevant in DevSecOps?
DevSecOps integrates security at every stage of the DevOps lifecycle. Data Contracts:
- Introduce schema validation and lineage tracing.
- Help enforce compliance and regulatory controls (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
- Reduce data drift and shadow data—which pose serious security risks.
- Enhance data observability, a key DevSecOps concern.
2. Core Concepts & Terminology
🔑 Key Terms
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Producer | System that generates and shares data. |
| Consumer | System or service that uses the data. |
| Schema Registry | Stores data contract definitions and versions. |
| Breaking Change | A change that violates the expectations set by the contract. |
| Validation Layer | Ensures conformance to schema rules. |
| Ownership | Producer teams are responsible for contract compliance. |
🔄 Role in the DevSecOps Lifecycle
| DevSecOps Stage | Role of Data Contracts |
|---|---|
| Plan | Define contracts as part of story acceptance criteria. |
| Develop | Contract definitions treated as code (Contract-as-Code). |
| Build/Test | CI validates data against contract before merge. |
| Release | Contracts tested in staging to prevent schema drift. |
| Deploy | Validated contracts deployed with data services. |
| Operate/Monitor | Data quality monitored via contracts. |
| Secure/Comply | Ensure only expected data is processed for auditing and compliance. |
3. Architecture & How It Works
🧱 Components
- Data Contract Definition (YAML/JSON) – describes schema, expectations.
- Validation Engine – runs checks at runtime or build time.
- Contract Registry – tracks versioned definitions.
- CI/CD Integrators – plug into GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, Jenkins, etc.
- Monitoring Layer – alerts on violations.
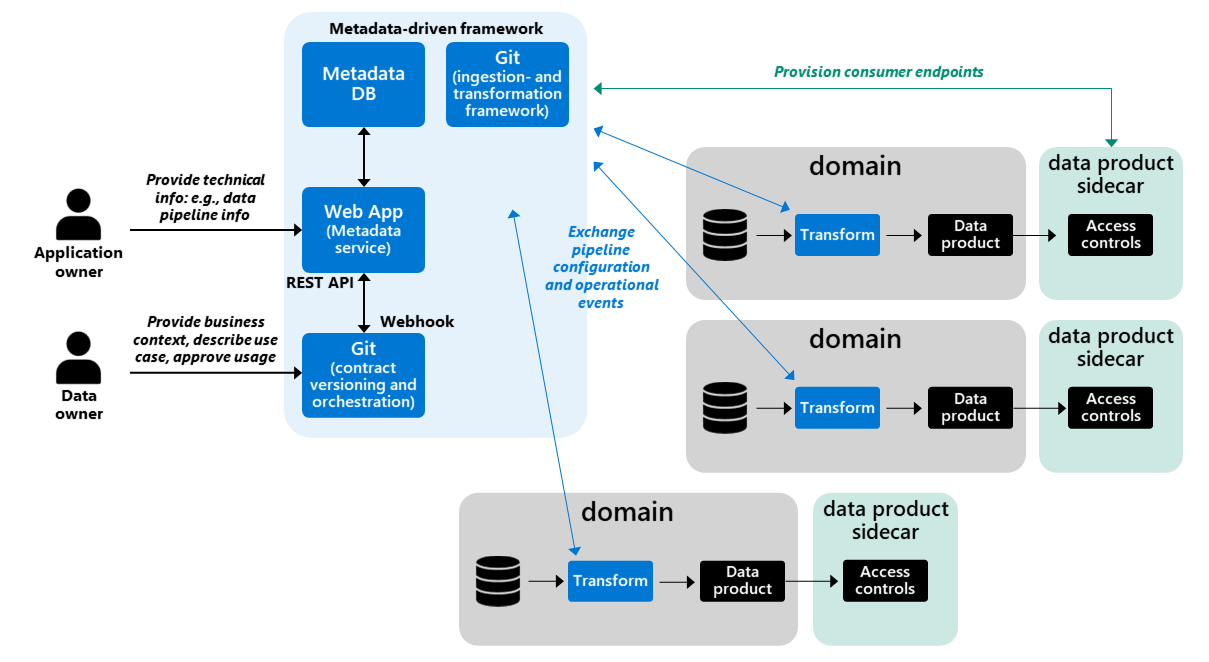
🔄 Internal Workflow
- Define: Developer writes a schema (e.g.,
customer_data_contract.yaml) - Validate: CI pipeline validates test data against schema.
- Publish: Contract pushed to a registry like Open Data Contract Standard.
- Enforce: Consumers must conform to this schema.
🧭 Architecture Diagram (Described)
[Producer Code]
↓
[Contract Definition] → [Schema Validator]
↓ ↓
[CI/CD Pipeline] → [Contract Registry]
↓
[Data Platform (e.g., Kafka, S3, Snowflake)]
↓
[Monitoring & Alerting]
☁️ Integration Points with CI/CD & Cloud
- CI: Contract validation as a step in Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI.
- CD: Prevents deployment if contract fails.
- Cloud: Integrates with Snowflake, BigQuery, Kafka, dbt, and Looker.
4. Installation & Getting Started
⚙️ Prerequisites
- Node.js or Python runtime
- Access to GitHub/GitLab CI/CD
- Basic understanding of YAML/JSON
- Data source (CSV, Kafka, etc.)
📦 Tools
🧪 Step-by-Step Guide
Step 1: Install CLI
npm install -g @data-contracts/cli
Step 2: Create a contract
datacontract init customer_data
Step 3: Define Schema (YAML)
name: customer_data
fields:
- name: customer_id
type: string
required: true
- name: signup_date
type: datetime
required: true
Step 4: Validate Sample Data
datacontract validate --file ./sample_customer_data.csv
Step 5: CI Integration (GitHub Actions)
# .github/workflows/datacontract.yml
name: Validate Data Contract
on: [push]
jobs:
validate:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- run: npm install -g @data-contracts/cli
- run: datacontract validate --file ./sample.csv
5. Real-World Use Cases
1️⃣ Data Governance in Financial Institutions
- Enforce strict schema validation on PII fields.
- Audit trail of every change in contract.
- Compliant with PCI DSS.
2️⃣ Secure Pipelines in Healthcare
- HIPAA-compliant contracts for sensitive data.
- Alerting system for unexpected schema changes.
3️⃣ Retail Analytics in eCommerce
- Maintain consistent schema for product inventory data.
- Auto-generate documentation from contracts.
4️⃣ Fraud Detection Pipelines
- Data contracts define strict expectations for transaction logs.
- Integrates with ML pipelines to reduce data leakage risks.
6. Benefits & Limitations
✅ Benefits
- 🔒 Security: Prevents schema drift, ensures data integrity.
- 🚦 Governance: Aligns with compliance frameworks (GDPR, HIPAA).
- 🤝 Collaboration: Establishes clear expectations between teams.
- ⚙️ Automation: Fits natively into CI/CD pipelines.
❌ Limitations
- ⏳ Initial setup overhead
- 📊 Requires producer buy-in and schema ownership
- 🧠 Learning curve for teams unfamiliar with schema-first design
- 🛠️ Limited tool maturity in some ecosystems
7. Best Practices & Recommendations
🔐 Security Tips
- Use signed contracts to prevent tampering.
- Enforce role-based access to modify contracts.
⚡ Performance & Maintenance
- Integrate contract testing early (shift-left).
- Version contracts semantically (e.g.,
v1.2.0).
📜 Compliance Alignment
- Log every schema change for audit.
- Align with data retention and data minimization policies.
🤖 Automation Ideas
- Auto-generate alerts on contract violations.
- Auto-generate downstream dbt models from contracts.
8. Comparison with Alternatives
| Feature | Data Contracts | Data Validation Only | Data Catalogs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Schema Versioning | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| CI/CD Integration | ✅ | ⚠️ Partial | ❌ |
| Contract-as-Code | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Security & Compliance Support | ✅ | ❌ | ⚠️ Partial |
| Data Lineage & Ownership | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
✅ When to Choose Data Contracts
- You have multiple producers/consumers sharing data.
- You need strict versioning, CI validation, and security.
- You operate in a regulated industry (finance, healthcare, etc.).
9. Conclusion
Data Contracts are becoming essential for building secure, maintainable, and trustworthy data pipelines in DevSecOps environments. By treating data definitions as code, they bring rigor, repeatability, and accountability to data workflows.
As teams scale, implementing Data Contracts offers:
- Enhanced trust in data
- Fewer production incidents
- Better DevSecOps alignment
📚 Resources & Community
- 🌐 Open Data Contract Standard
- 📘 GitHub CLI: Data Contract CLI
- 🧑💻 Community: Data Contracts on Slack
- 🛠 Example Repo: https://github.com/datacontracts/examples