1. Introduction & Overview
What is Data Encryption?
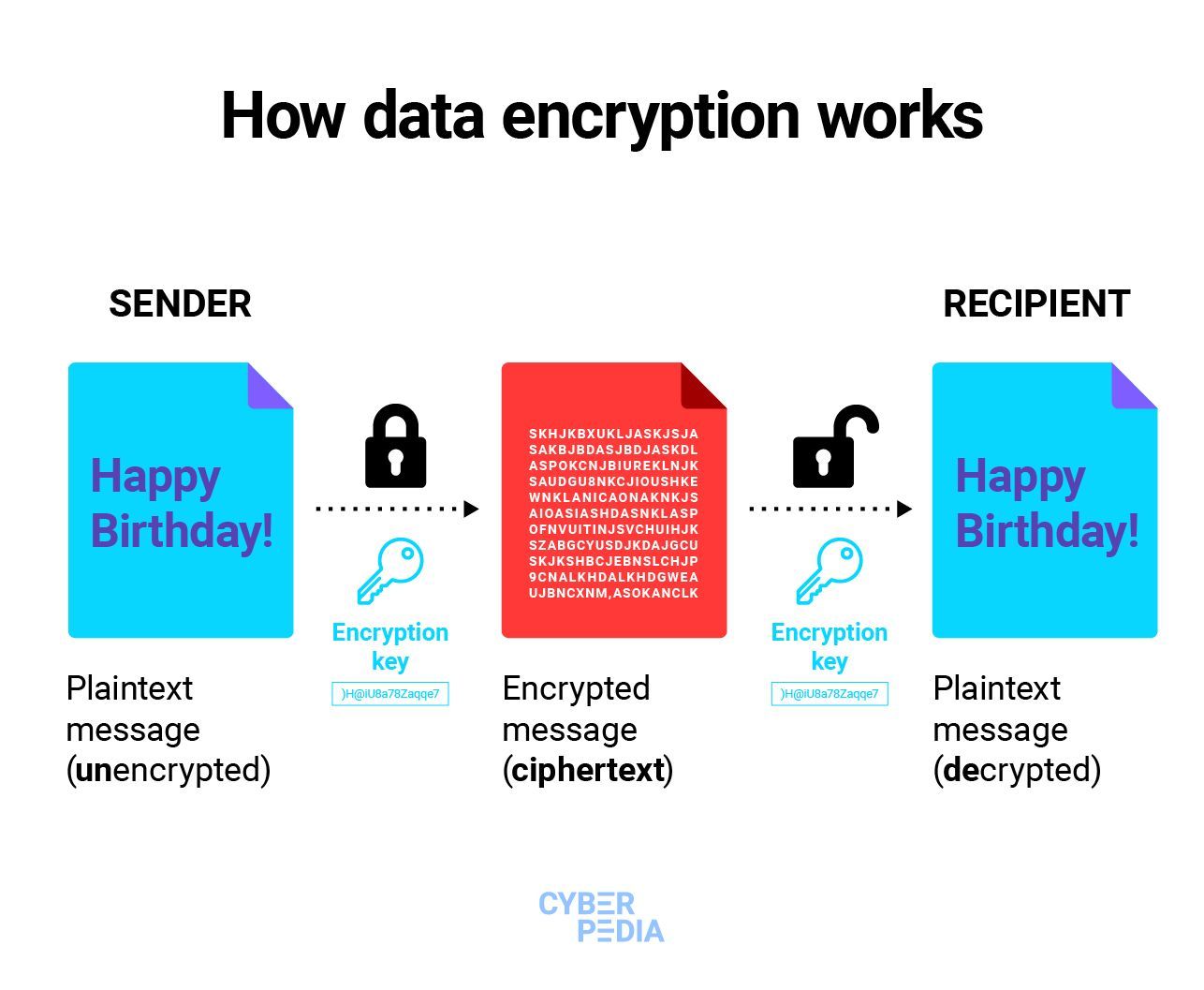
Data encryption is the process of converting readable (plaintext) data into an unreadable format (ciphertext) using cryptographic algorithms. Only authorized parties with the right decryption key can convert it back to its original form.
In DataOps, where data flows continuously across pipelines, CI/CD systems, and cloud platforms, encryption ensures data confidentiality, integrity, and compliance.
History / Background
- Ancient Times – Encryption began with Caesar Cipher (~58 BC).
- 1970s – DES (Data Encryption Standard) introduced by IBM and adopted by NIST.
- 1990s – RSA, AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) became global standards.
- Modern Era – Cloud-native encryption (AWS KMS, Azure Key Vault, HashiCorp Vault) integrated directly into DataOps pipelines.
Why is it Relevant in DataOps?
In a DataOps environment, data moves rapidly between:
- Databases → ETL tools → Data Lakes → Analytics → AI models.
Each stage is a potential breach point. Encryption helps to:
- Protect PII, PHI, financial data.
- Ensure compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS).
- Secure data pipelines from insider threats and cyberattacks.
2. Core Concepts & Terminology
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Plaintext | Original readable data. |
| Ciphertext | Encrypted, unreadable version of data. |
| Key | Secret value used to encrypt/decrypt. |
| Symmetric Encryption | Same key for encryption & decryption (e.g., AES). |
| Asymmetric Encryption | Public/private key pairs (e.g., RSA). |
| Encryption in Transit | Securing data while moving (TLS/SSL). |
| Encryption at Rest | Securing stored data (AES-256, disk-level encryption). |
| KMS (Key Management Service) | Manages encryption keys (AWS KMS, Azure Key Vault). |
How It Fits into the DataOps Lifecycle
- Data Ingestion – Encrypt sensitive data before moving into pipelines.
- Data Transformation – Apply encryption/decryption for masked analytics.
- Data Storage – Store encrypted files/databases.
- Data Delivery – Ensure APIs and ML models use encrypted endpoints.
- Monitoring – Logs and audit trails should also be encrypted.
3. Architecture & How It Works
Components
- Encryption Algorithms (AES, RSA, SHA for hashing)
- Key Management System (KMS) – Generates, rotates, stores keys securely
- Data Pipeline Stages – Points where encryption/decryption occurs
- Access Controls & IAM – Ensures only authorized services/users decrypt data
Internal Workflow
- Data enters pipeline → Encryption applied (AES/RSA).
- Encrypted data stored in databases/data lakes.
- If required for analytics → Decryption with key access.
- Keys managed by KMS/Vault with policies & rotation.
Architecture Diagram (Text Description)
[Data Source] → [Ingestion Layer w/ Encryption] → [ETL/Processing]
→ [Data Lake / Warehouse (Encrypted at Rest)] → [Analytics/BI Tools]
↑
[Key Management Service (KMS)]
Integration Points with CI/CD or Cloud Tools
- CI/CD: Encrypt secrets in GitHub Actions, Jenkins, GitLab CI.
- Cloud:
- AWS – S3 SSE, RDS encryption, AWS KMS.
- Azure – Azure Key Vault, Storage Encryption.
- GCP – Cloud KMS, CMEK (Customer-Managed Encryption Keys).
- HashiCorp Vault – Enterprise-grade secret & key management for pipelines.
4. Installation & Getting Started
Prerequisites
- Linux/Mac machine
- Python or Bash scripting knowledge
- Installed OpenSSL or GPG
- Access to a cloud account (AWS/Azure/GCP)
Hands-On: Encrypt & Decrypt using OpenSSL
Step 1 – Encrypt a file:
openssl enc -aes-256-cbc -salt -in data.txt -out data.txt.enc -k SECRET_KEY
Step 2 – Decrypt a file:
openssl enc -aes-256-cbc -d -in data.txt.enc -out data.txt -k SECRET_KEY
AWS KMS Example (Encrypt/Decrypt)
Encrypt using AWS KMS CLI:
aws kms encrypt \
--key-id alias/my-key \
--plaintext fileb://data.txt \
--output text \
--query CiphertextBlob | base64 --decode > data.enc
Decrypt using AWS KMS CLI:
aws kms decrypt \
--ciphertext-blob fileb://data.enc \
--output text \
--query Plaintext | base64 --decode > data.txt
5. Real-World Use Cases
Example 1: Healthcare DataOps
Encrypting patient medical records (HIPAA compliance) before uploading to a Data Lake.
Example 2: Financial Transactions
Banks encrypt credit card details during ETL pipelines for PCI DSS compliance.
Example 3: E-commerce Analytics
Encrypt customer PII while sharing behavioral analytics with third-party ML models.
Example 4: Cloud Data Migration
Encrypt datasets before moving them between AWS S3 and Azure Blob Storage.
6. Benefits & Limitations
Key Advantages
- Data confidentiality & compliance (GDPR, HIPAA).
- Secure CI/CD pipelines.
- Reduces insider threat risks.
- Prevents man-in-the-middle attacks.
Common Limitations
- Performance overhead (encryption/decryption slows pipelines).
- Key management complexity.
- Cost of enterprise KMS solutions.
- Possible misconfiguration → security loopholes.
7. Best Practices & Recommendations
- Use AES-256 or stronger encryption.
- Rotate keys regularly (automate via AWS KMS, Vault).
- Apply encryption both in-transit (TLS/SSL) and at-rest.
- Integrate secrets management (Vault, SOPS, AWS Secrets Manager).
- Implement IAM policies → Least Privilege access.
- Monitor & audit encryption activities.
8. Comparison with Alternatives
| Approach | When to Use | Example Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Protect sensitive data end-to-end | AES, RSA, AWS KMS |
| Masking | Hide data for testing/analytics | Informatica, Delphix |
| Tokenization | Replace data with tokens | Protegrity, Thales |
| Hashing | One-way protection (passwords) | SHA-256, bcrypt |
Choose Encryption when you need reversible protection for regulated, sensitive data in DataOps pipelines.
9. Conclusion
Data Encryption is the foundation of trust in DataOps pipelines. It ensures secure handling of data across ingestion, storage, transformation, and delivery phases. With the rise of cloud-native DataOps and regulatory compliance, encryption will remain central to enterprise data workflows.
Future Trends
- Quantum-safe encryption.
- AI-assisted key management.
- Zero-trust data pipelines.
Next Steps
- Implement AES-256 encryption in your pipelines.
- Integrate with AWS KMS / HashiCorp Vault.
- Automate key rotation and compliance checks.
References
- NIST Cryptography Standards
- AWS KMS Documentation
- HashiCorp Vault Docs