1. Introduction & Overview
What is Amazon Redshift?
Amazon Redshift is a fully managed, petabyte-scale cloud data warehouse service provided by AWS. It allows for fast query performance using SQL-based interfaces on large volumes of structured and semi-structured data.
History & Background
- Launched by AWS in 2012
- Based on ParAccel, a columnar storage technology
- Continuously evolving with features like RA3 nodes, AQUA (Advanced Query Accelerator), and serverless deployment
Why is Redshift Relevant in DevSecOps?
DevSecOps integrates security into DevOps workflows. Redshift plays a crucial role in:
- Centralized logging and audit data analysis
- Monitoring behavioral anomalies using security telemetry
- Real-time compliance reporting
- Enabling automation and alerts based on security events
2. Core Concepts & Terminology
Key Terms and Definitions
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Cluster | A collection of Redshift nodes (compute + leader node) |
| Node | A single computing instance within a cluster |
| Columnar Storage | Stores data by columns for faster analytics |
| Spectrum | Redshift’s ability to query data in S3 directly |
| AQUA | Hardware-accelerated cache for faster query performance |
| WLM | Workload Management – manages query priorities and concurrency |
| IAM | Identity and Access Management to secure Redshift resources |
| VPC | Virtual Private Cloud to control Redshift network access |
How Redshift Fits Into the DevSecOps Lifecycle
| DevSecOps Phase | Redshift Role |
|---|---|
| Plan | Analyze previous incidents for secure design decisions |
| Develop | Integrate telemetry for logging and event analysis |
| Build | Validate configurations via compliance checks |
| Test | Analyze test results for vulnerabilities |
| Release | Log releases and anomalies |
| Deploy | Validate against compliance rules and detect risks |
| Operate | Real-time data analytics and alerts |
| Monitor | Continuous anomaly detection and compliance tracking |
3. Architecture & How It Works
Components of Redshift
- Leader Node: Coordinates query distribution and aggregates results
- Compute Nodes: Perform the actual data processing
- Redshift Spectrum: Extends analytics to S3
- Redshift Serverless: Run analytics without provisioning infrastructure
- VPC & Security Groups: Network security boundary

Internal Workflow (Simplified)
- Client sends SQL query to the leader node
- Leader node parses and creates an execution plan
- Query is distributed to compute nodes
- Results are aggregated and returned
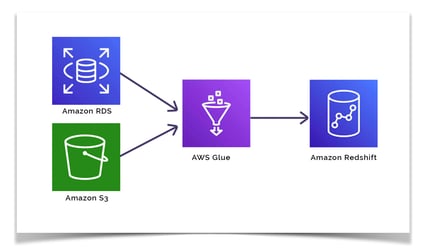
Architecture Diagram (Descriptive)
Client
|
v
[Leader Node]
|
v
[Compute Node 1] [Compute Node 2] ... [Compute Node N]
|
v
[Amazon S3 via Redshift Spectrum (Optional)]
Integration Points with CI/CD or Cloud Tools
- CI/CD: Integrate with Jenkins, GitHub Actions for data validation and compliance checks
- Security Tools: GuardDuty, CloudTrail, AWS Config for anomaly detection
- Monitoring: Amazon CloudWatch for logs and alarms
- IaC: Use Terraform/CloudFormation for Redshift provisioning
4. Installation & Getting Started
Prerequisites
- AWS account
- IAM role with Redshift and S3 access
- VPC, subnet group, and security group setup
Step-by-Step Setup
1. Create IAM Role
aws iam create-role --role-name RedshiftRole --assume-role-policy-document file://trust-policy.json
aws iam attach-role-policy --role-name RedshiftRole --policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonRedshiftFullAccess
2. Launch a Redshift Cluster (AWS Console or CLI)
aws redshift create-cluster \
--cluster-identifier devsecops-cluster \
--node-type ra3.xlplus \
--master-username admin \
--master-user-password MySecurePass123 \
--cluster-type single-node \
--iam-roles arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/RedshiftRole
3. Configure Security Group and Access
- Allow inbound on port
5439 - Restrict to specific IPs or VPC CIDR
4. Connect Using SQL Client
-- Connect using DBeaver, pgAdmin, or SQL Workbench/J
SELECT * FROM pg_user;
5. Real-World Use Cases
1. Security Incident Investigation
- Aggregate logs from CloudTrail and analyze IAM actions
- Identify unusual access patterns
2. Compliance Dashboards
- Daily snapshots of security configurations
- GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO compliance queries
3. DevSecOps Automation
- CI/CD pipeline integration to store and analyze test/scan results
- Trigger alerts for non-compliant builds
4. Financial Sector Example
- Analyze trade logs for anomaly detection in fintech platforms
- Detect fraudulent patterns using Redshift ML + data pipelines
6. Benefits & Limitations
Key Advantages
- 🔄 Seamless integration with AWS ecosystem
- ⚡ High performance with columnar storage and parallel execution
- 🔒 Strong security controls with encryption, IAM, VPC, and audit logging
- 🚫 Serverless option reduces operational overhead
Limitations
| Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost | Can be expensive if not optimized |
| Query complexity | Needs optimization for large joins/aggregates |
| Cold start in serverless | May introduce delay in query start |
| Limited to AWS ecosystem | Not easily portable to other cloud platforms |
7. Best Practices & Recommendations
Security Tips
- Enable VPC-based access controls
- Use KMS encryption for data at rest
- Enable audit logging and stream to S3/CloudWatch
- Rotate IAM credentials frequently
Performance & Maintenance
- Use sort and distribution keys wisely
- Schedule vacuum and analyze commands
- Enable concurrency scaling
Compliance & Automation
- Integrate with AWS Config for compliance auditing
- Automate Redshift creation via Terraform or CloudFormation
- Export logs to S3 and analyze with Athena or Redshift Spectrum
8. Comparison with Alternatives
| Feature / Tool | Amazon Redshift | Snowflake | BigQuery |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Platform | AWS | Multi-cloud | GCP |
| Security | AWS-native IAM, VPC | Advanced role control | IAM, org policies |
| Cost Model | Node/hour or serverless | Pay-per-second | Pay-per-query |
| DevSecOps Fit | Tight AWS integration | Moderate | Strong for GCP users |
When to Choose Redshift
- Already using AWS-based DevSecOps tools
- Need high-speed performance on large workloads
- Desire tight control over network security
9. Conclusion
Amazon Redshift serves as a powerful analytics and compliance engine in modern DevSecOps pipelines. Its scalability, performance, and security make it suitable for real-time insights into security posture, anomaly detection, and compliance reporting.
As Redshift evolves—with serverless deployment, AQUA acceleration, and ML support—its role in DevSecOps will only grow stronger.