1. Introduction & Overview
What is Integration Testing?
Integration Testing is a level of software testing where individual units or components are combined and tested as a group to expose faults in the interactions between them. It validates that multiple components work together correctly after being integrated.
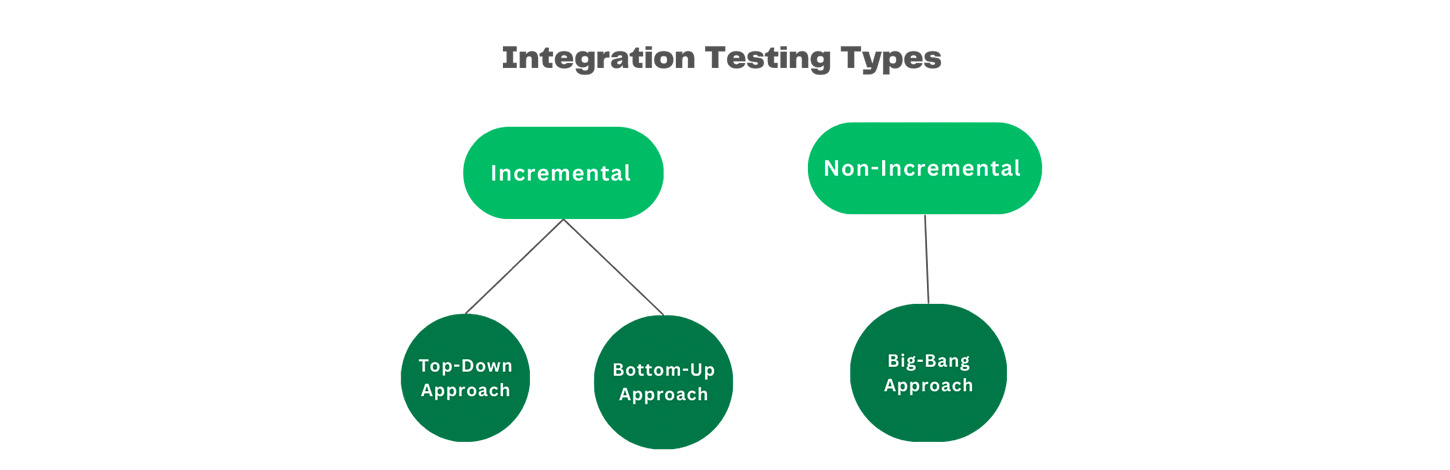
- Focus: Interfaces and data flow between modules.
- Position in Testing Pyramid: Above Unit Testing, below System Testing.
History and Background
- 1970s: Emerged alongside modular programming to ensure inter-module communication works.
- 2000s Onwards: With Agile, CI/CD, and DevSecOps, integration testing became continuous and automated.
- Present: Plays a central role in pipelines, particularly in microservices, APIs, and container-based architectures.
Why Is It Relevant in DevSecOps?
- Security validation between components and services (e.g., secure API communication).
- Ensures shifts-left testing, validating integrations early in CI/CD.
- Enables compliance checks, policy enforcement, and vulnerability detection across connected modules.
2. Core Concepts & Terminology
Key Terms and Definitions
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Test Stub | Simulates a lower-level module’s behavior. |
| Test Driver | Simulates a higher-level module that calls the component under test. |
| Top-down testing | Testing starts from top-level modules and integrates downward. |
| Bottom-up testing | Testing starts with low-level modules and integrates upward. |
| Sandwich testing | Combines both top-down and bottom-up approaches. |
| Continuous Testing | Automated execution of tests as part of the CI/CD pipeline. |
How It Fits Into the DevSecOps Lifecycle
Integration testing aligns with key phases of the DevSecOps pipeline:
| DevSecOps Phase | Role of Integration Testing |
|---|---|
| Plan | Define interface contracts and security policies. |
| Develop | Run integration tests for each merged feature. |
| Build | Integrate test suites in the CI pipeline. |
| Test | Validate services, APIs, and third-party components. |
| Release | Gate releases based on test results. |
| Deploy | Post-deployment smoke tests. |
| Operate | Monitor for integration anomalies. |
| Monitor | Feed back insights for continuous improvement. |
3. Architecture & How It Works
Components
- Application Modules: Units that must interact (e.g., microservices).
- Middleware/Communication Layers: API gateways, message brokers.
- Test Harness: Framework or tool that drives integration test execution.
- Mocks/Stubs: Replace unavailable components or simulate external APIs.
Internal Workflow
- Module Development: Teams build components independently.
- Integration Environment: Spin up test environments (e.g., Docker, Kubernetes).
- Execution: Run integration tests after successful unit tests.
- Validation: Verify service contracts, data flows, error handling.
- Security Gates: Check for secrets exposure, API policy violations.
Architecture Diagram (Descriptive)
[ Service A ] <--API--> [ Service B ] <--DB--> [ Database ]
| |
+----> [ Integration Test Suite ] <----+
|
[Security Checks]
Integration Points with CI/CD and Cloud Tools
- CI Tools: Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI – Trigger integration tests on merges.
- Cloud Environments: AWS CodePipeline, Azure DevOps – Deploy isolated environments for test execution.
- Security Tools: Snyk, Aqua, or Trivy – Integrated to scan during test phases.
4. Installation & Getting Started
Basic Setup or Prerequisites
- A project with modular codebase or microservices.
- CI/CD system (e.g., GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, Jenkins).
- Docker or Kubernetes (optional for environment spin-up).
- A testing framework like:
- JUnit/TestNG (Java)
- pytest (Python)
- Mocha (JavaScript)
- Postman/Newman or REST Assured for API integration testing
Step-by-Step: Example with pytest and Docker
- Install Python and
pytest
pip install pytest requests
2. Write a sample integration test
import requests
def test_api_integration():
response = requests.get("http://localhost:8000/api/health")
assert response.status_code == 200
3. Docker Compose for Integration Testing
version: '3.8'
services:
app:
build: .
ports:
- "8000:8000"
test:
build:
context: .
command: ["pytest", "tests/integration/"]
depends_on:
- app
4. CI/CD Pipeline Snippet (GitHub Actions)
jobs:
integration-test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Run Integration Tests
run: docker-compose up --abort-on-container-exit
5. Real-World Use Cases
Use Case 1: Microservices Communication
- Validate RESTful API contract between
User ServiceandBilling Service. - Enforce schema validation, JWT auth, and rate-limiting policies.
Use Case 2: CI/CD Security Pipeline
- Run integration tests post-build but pre-deployment.
- Test secrets retrieval from vaults like HashiCorp Vault or AWS Secrets Manager.
Use Case 3: Cloud-Native Applications
- Integration tests spin up services using Kubernetes namespaces.
- Test communication over service meshes like Istio (e.g., mTLS enforcement).
Use Case 4: E-commerce Checkout Flow
- Validate end-to-end flow: Product Service → Cart → Payment Gateway.
- Simulate 3rd-party payment APIs and mock failures.
6. Benefits & Limitations
Key Advantages
- Early bug detection in component interactions.
- Security validation at communication boundaries.
- Ensures reliability of third-party services and APIs.
- Boosts confidence before deployments.
Common Challenges
- Environment setup complexity (e.g., dependency resolution).
- Flaky tests due to timing issues or network instability.
- Slow execution vs. unit tests.
- False positives/negatives without good mocking/stubbing.
7. Best Practices & Recommendations
Security, Performance, Maintenance
- Use network segmentation in test environments to isolate components.
- Enable TLS/mTLS during tests for realistic security validation.
- Mock external APIs to prevent rate limiting and ensure test consistency.
- Centralize logs for test analysis.
Compliance & Automation
- Embed policy-as-code validation (e.g., OPA/Rego policies).
- Automate secrets injection using sealed secrets or service accounts.
- Log test results to SIEM or compliance dashboards.
8. Comparison with Alternatives
| Approach | Pros | Cons | When to Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unit Testing | Fast, isolated | Doesn’t catch integration issues | Early-stage dev |
| Integration Testing | Validates module interaction, security | Slower, needs setup | After unit tests, pre-release |
| System Testing | End-to-end validation | Too broad for early bugs | Pre-deploy validation |
| Contract Testing | Precise schema enforcement | Limited to API-level only | Microservices/API-heavy systems |
9. Conclusion
Integration Testing is essential in any DevSecOps pipeline to ensure secure, stable, and interoperable components. It acts as a gatekeeper between individual development efforts and holistic system behavior, especially vital in cloud-native and microservices environments.
Future Trends
- AI-based test generation
- Self-healing tests
- Shift-right testing with runtime integrations