📘 1. Introduction & Overview
🔍 What is Data Encryption?
Data Encryption is the process of converting plain text into a coded form (ciphertext) to prevent unauthorized access. Only parties with a decryption key can revert the encrypted data back to its original form.

🧭 History / Background
- Ancient roots: Cryptography dates back to ancient Egypt (e.g., hieroglyphs).
- World Wars: The Enigma machine during WWII advanced modern cryptography.
- Modern age: With the rise of the internet, digital encryption evolved (e.g., AES, RSA, TLS).
- Today: Encryption is foundational in zero trust models and cloud-native DevSecOps.
💡 Why Is It Relevant in DevSecOps?
- DevSecOps integrates security early and continuously in CI/CD pipelines.
- Encryption ensures confidentiality, integrity, and compliance across the software lifecycle.
- Regulatory requirements (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR, PCI-DSS) mandate strong encryption policies.
📚 2. Core Concepts & Terminology
🧩 Key Terms
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Plaintext | The original readable data |
| Ciphertext | Encrypted, unreadable data |
| Key | A secret value used to encrypt/decrypt data |
| Symmetric Encryption | Same key for encryption and decryption (e.g., AES) |
| Asymmetric Encryption | Different keys: public (encrypt) and private (decrypt) (e.g., RSA) |
| TLS | Transport Layer Security — secures communication between systems |
| KMS | Key Management Service — manages cryptographic keys |
🔁 How It Fits Into the DevSecOps Lifecycle
- Plan & Code: Secrets scanning to avoid hardcoded keys.
- Build & Test: Encrypt secrets (e.g., using GitHub Actions or HashiCorp Vault).
- Release & Deploy: TLS encryption during deployment.
- Operate & Monitor: Monitor encrypted logs; rotate keys regularly.
🏗️ 3. Architecture & How It Works
🧱 Core Components
- Encryption Algorithm: Defines how data is transformed (e.g., AES-256, RSA-2048).
- Encryption Keys: Stored securely in tools like AWS KMS, Azure Key Vault, or HashiCorp Vault.
- Key Management: Rotation, storage, and revocation of keys.
- Integration Layer: SDKs or plugins to integrate encryption in apps and CI/CD.
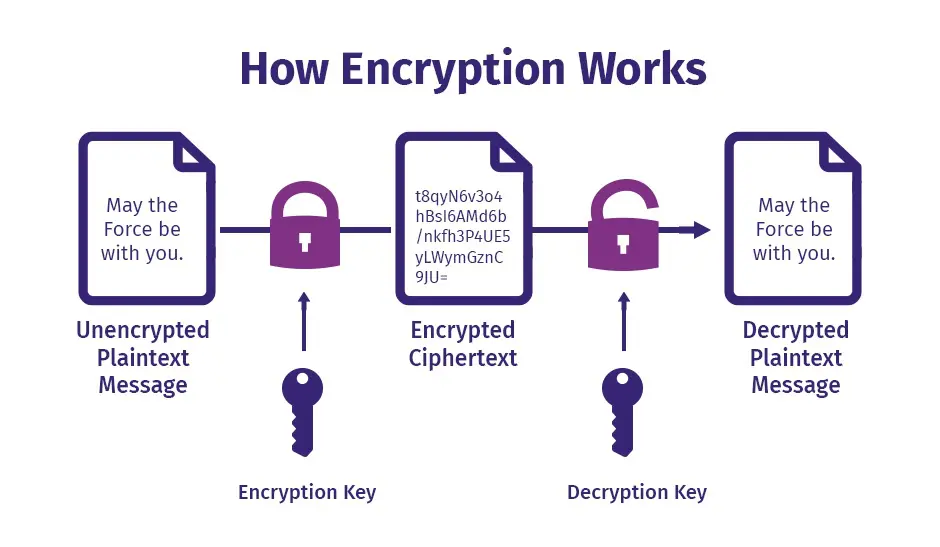
🔄 Internal Workflow
- Data Input: App or system processes data.
- Key Fetch: Retrieve encryption key securely from vault.
- Encrypt: Convert plaintext to ciphertext using the key.
- Transmit/Store: Securely store or send the encrypted data.
- Decrypt: Authorized entity retrieves and decrypts data.
🖼️ Architecture Diagram (Described)
[App Server] → [Encryption SDK/API] → [Key Vault (KMS)] → [Encrypted Storage / DB]
↘
[Logging & Monitoring]
⚙️ Integration Points
- CI/CD: Encrypt secrets in GitHub Actions, Jenkins, GitLab.
- Cloud Providers:
- AWS: AWS KMS + IAM Roles
- Azure: Azure Key Vault with RBAC
- GCP: Cloud KMS + IAM Policies
🚀 4. Installation & Getting Started
📋 Prerequisites
- Programming knowledge (e.g., Python, Node.js, Go)
- Access to cloud provider or KMS (e.g., AWS, Azure)
- CLI tools (e.g., AWS CLI)
🛠️ Step-by-Step Setup (Example: Encrypt Data with AWS KMS + Python)
Step 1: Setup AWS CLI
aws configure
Step 2: Create KMS Key
aws kms create-key --description "DevSecOps demo key"
Note the KeyId from the output.
Step 3: Encrypt Data
aws kms encrypt \
--key-id <your-key-id> \
--plaintext fileb://data.txt \
--output text \
--query CiphertextBlob
Step 4: Decrypt Data
aws kms decrypt \
--ciphertext-blob fileb://ciphertext.txt \
--output text \
--query Plaintext
🌍 5. Real-World Use Cases
🧪 Use Case 1: Secrets Management in CI/CD
- Encrypt secrets in GitHub Actions using GPG or HashiCorp Vault.
- Prevent accidental leaks of passwords or tokens in pipelines.
🏥 Use Case 2: Healthcare (HIPAA Compliance)
- Encrypt patient data before storing in cloud (e.g., AWS S3 with server-side encryption).
💳 Use Case 3: Finance Sector (PCI-DSS)
- Tokenize and encrypt credit card numbers in real-time using symmetric encryption.
🛡️ Use Case 4: Zero Trust Microservices
- All service-to-service communications over TLS 1.3 with mutual authentication.
- Dynamic secrets and certificates through SPIRE + Vault.
✅ 6. Benefits & Limitations
🎯 Key Benefits
- 🔐 Confidentiality: Keeps sensitive data safe even if leaked.
- 🛡️ Compliance: Meets regulatory requirements.
- 🔄 Automated Key Rotation: Reduces manual work.
- ☁️ Cloud-Native Support: Fully supported by AWS, Azure, GCP.
⚠️ Common Limitations
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Key Mismanagement | Compromised keys break entire encryption. |
| Performance Overhead | High CPU usage on large datasets. |
| Complexity | Requires strong understanding & governance. |
| Human Error | Mistakes in key sharing or logging plaintext. |
🧠 7. Best Practices & Recommendations
🔒 Security Tips
- Never store keys in source code.
- Use hardware security modules (HSM) or KMS.
- Enable automatic key rotation.
- Monitor access logs and set up alerts.
🧪 Performance & Maintenance
- Use streaming encryption for large files.
- Encrypt at field-level, not just whole database.
✅ Compliance Alignment
| Standard | Encryption Requirement |
|---|---|
| HIPAA | Data at rest and in transit |
| GDPR | Pseudonymization and encryption |
| PCI-DSS | Encryption of cardholder data |
🤖 Automation Ideas
- Integrate Vault into GitLab CI/CD pipelines.
- Rotate secrets every X days automatically using Terraform + Vault.
🔄 8. Comparison with Alternatives
| Feature | Data Encryption | Tokenization | Masking |
|---|---|---|---|
| Use Case | Security & Compliance | Reducing exposure | Dev/Test environments |
| Reversibility | Yes (with keys) | Sometimes | No |
| Compliance | High | High | Low |
| Speed | Slower (CPU intensive) | Faster | Fast |
🏁 When to Use Data Encryption?
- When dealing with highly sensitive data.
- When compliance mandates encrypted storage/transmission.
- When integrating DevSecOps pipelines with cloud-native security.
🏁 9. Conclusion
Data Encryption is not just a technical requirement — it’s a strategic pillar of secure software delivery in DevSecOps. By integrating encryption into your SDLC, you:
- Secure data proactively.
- Meet compliance confidently.
- Build user trust and reduce breaches.
🔗 Useful Resources
- 🔗 AWS KMS Docs
- 🔗 HashiCorp Vault
- 🔗 OWASP Cryptographic Storage Cheat Sheet
- 🔗 DevSecOps GitHub Actions Guide
Category: